ISA
From NaplesPU Documentation
Contents
Instructions Format
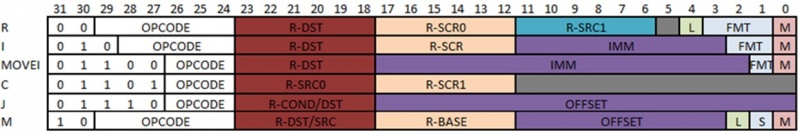
The nu+ instructions have a fixed length of 32 bits. They are grouped in seven types:
- The R type includes the logical and arithmetic operations and memory operations.
- The I type includes the logical and arithmetic operations between a register operand and an immediate operand.
- The MOVEI type includes the load operations of an immediate operand in a register.
- The C type used for control operations and for synchronization instructions.
- The JR type includes jump instructions.
- The M type includes the instructions used to access memory.
- The M-poly type is used for memory instructions which uses a polyhedral access pattern.
R type instructions
- RR (Register to Register) has a destination register and two source registers.
- RI (Register Immediate) has a destination register and one source registers and an immediate encoded in the instruction word.
| Mnemonic | Opcode | Meaning | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|
| or | 1 | or | Rb |
| and | 2 | and | Rd = Ra & Rb |
| xor | 3 | xor | Rd = Ra ^ Rb |
| add | 4 | addition | Rd = Ra + Rb |
| sub | 5 | subtraction | Rd = Ra – Rb |
| mull | 6 | multiplication | Rd = Ra * Rb |
| mulh | 7 | high multiply | Rd = Ra * Rb |
| mulhu | 8 | high multiply unsigned | Rd = Ra * Rb |
| ashr | 9 | arithmetic shift right | Rd = Ra ‘>> Rb |
| shr | 10 | shift right | Rd = Ra >> Rb |
| shl | 11 | shift left | Rd = Ra << Rb |
| clz | 12 | count leading zeros | |
| ctz | 13 | count trailing zeros | |
| shuffle | 24 | vector shuffle | Rd[i] = Ra[Rb[i]] |
| getlane | 25 | Get lane from vector | Rd = Ra[Rb] |
| move | 32 | move register | Rd = Ra |
| add_f | 33 | floating point add | Rd = Ra + Rb |
| sub_f | 34 | floating point sub | Rd = Ra – Rb |
| mul_f | 35 | floating point multiplication | Rd = Ra * Rb |
| div_f | 36 | floating point division | Rd = Ra / Rb |
| sext8 | 43 | sign extend 8 bits | |
| sext16 | 44 | sign extend 16 bits | |
| sext32 | 45 | sign extend 32 bits | |
| f32tof64 | 46 | cast float to double | |
| f64tof32 | 47 | cast double to float | |
| i32tof32 | 48 | cast integer to float | |
| f32toi32 | 49 | cast float to integer |
I type instructions
MOVEI type instructions
MVI (Move Immediate) has a destination register and a 16 bit instruction encoded immediate.
C type instructions
JR type instructions
J type instructions
M type instructions
MEM (Memory Instruction) has a destination/source field, in case of load the first register asses the destination register, otherwise in case of store the first register contains the store value. Next in both cases there is the base address and the immediate. The sum of base address and immediate will give the effective memory address.